The Role of Leadership in Implementing an Effective Process Safety Management System
Introduction
Effective Process Safety Management (PSM) is essential for industries dealing with hazardous processes. While technical measures and risk assessments play a significant role, leadership is the driving force behind a successful implementation of safety strategies. Leadership ensures that safety policies are not just documented but actively practiced and continuously improved. This article explores the role of leadership in implementing an effective PSM system and how it influences workplace safety.
Why Leadership is Crucial in Process Safety Management?
Leadership is responsible for establishing a safety culture, ensuring compliance, and fostering continuous improvements in industrial safety. An engaged leadership ensures that safety protocols are not limited to documentation but are ingrained into daily operations. Leaders set the tone, expectations, and accountability for process safety across all levels of an organization.
Key Responsibilities of Leadership in PSM Implementation
- Defining Clear Safety Objectives
- Leaders must develop and communicate a comprehensive safety vision for the organization.
- Ensuring that PSM goals align with operational and business objectives.
- Allocating Resources for Safety Initiatives
- Providing necessary investments in safety technologies, training, and personnel.
- Supporting continuous improvement by incorporating insights from Safety Audits.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
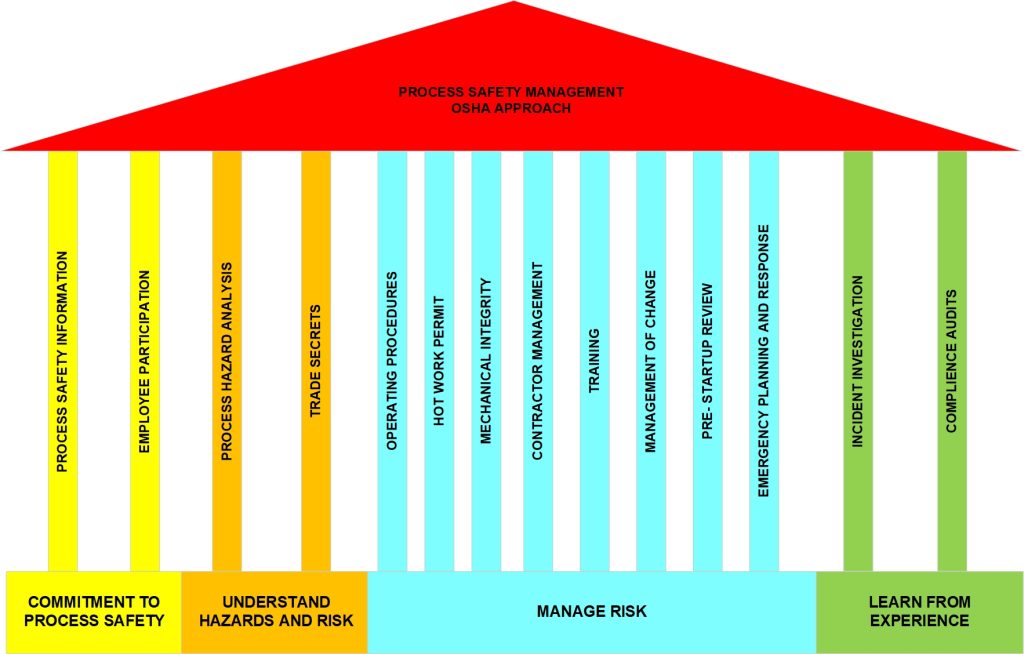
- Compliance with industry regulations like OSHA PSM standards (29 CFR 1910.119).
- Regularly reviewing safety policies and adopting improvements.
- Encouraging Employee Involvement in Safety Processes
- Leaders should engage employees in safety discussions.
- Conducting HAZOP Studies to analyze risks and take preventive actions.
- Organizing periodic Hazop Study reviews.
Establishing a Safety-First Culture
A safety-first culture is essential for successful Process Safety Management implementation. Leaders should foster an environment where safety is prioritized over operational efficiency.
Ways to Establish a Strong Safety Culture
- Encouraging open communication about safety concerns.
- Rewarding employees who proactively identify risks.
- Conducting regular Fire Audits to mitigate fire hazards.
- Implementing near-miss reporting mechanisms to improve incident prevention.
Training and Development for Safety Leadership
A knowledgeable leadership team must continuously update its expertise in PSM. Leadership training programs should include:
- Process hazard analysis techniques.
- Regulatory compliance training.
- Incident investigation and response protocols.
- Collaboration with a Safety Consultant to refine safety strategies.
Monitoring and Improving PSM Effectiveness
To ensure continuous improvements, organizations must establish a system for monitoring safety performance.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for PSM
- Reduction in process-related incidents.
- Compliance with regulatory audits.
- Employee participation in safety programs.
- Effectiveness of emergency response drills.
Regular assessments and Process Safety Management reviews help refine strategies and identify improvement areas.
Conclusion
Leadership is the backbone of effective Process Safety Management. A proactive approach that includes clear objectives, resource allocation, employee engagement, and continuous monitoring ensures a robust safety framework. Leaders must champion a safety-first mindset to drive industrial safety and protect personnel, assets, and the environment.